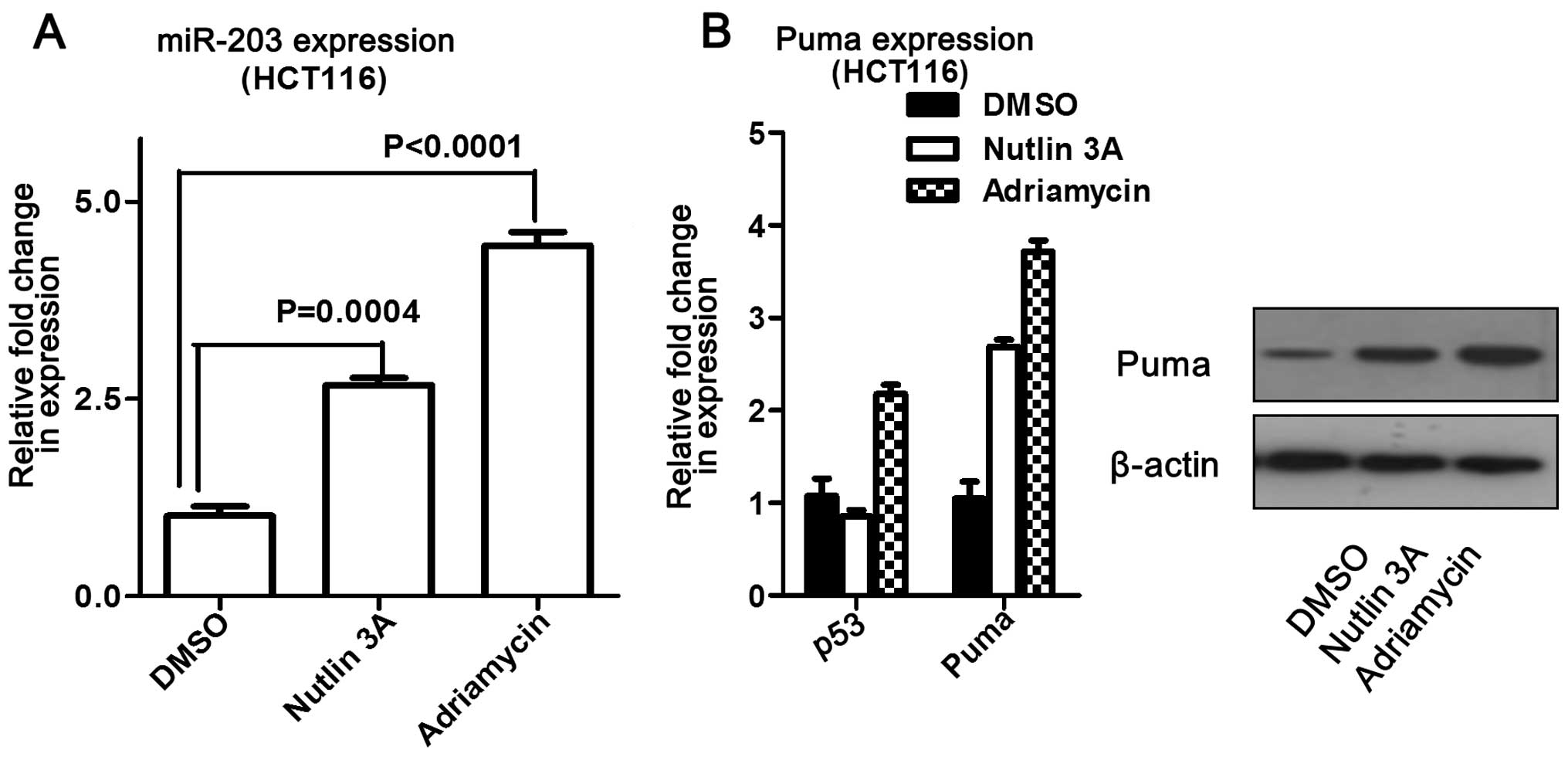
Wild-Type p53 Promotes Cancer Metabolic Switch by Inducing PUMA-Dependent Suppression of Oxidative Phosphorylation

Regulation of p53 Stability and Function in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells* - Journal of Biological Chemistry

A, p53-KO HCT116 cells were incubated with aciculatin (5–10 µM) for 48... | Download Scientific Diagram
Molecular crosstalk between ferroptosis and apoptosis: emerging role of ER stress-induced p53-independent PUMA expression
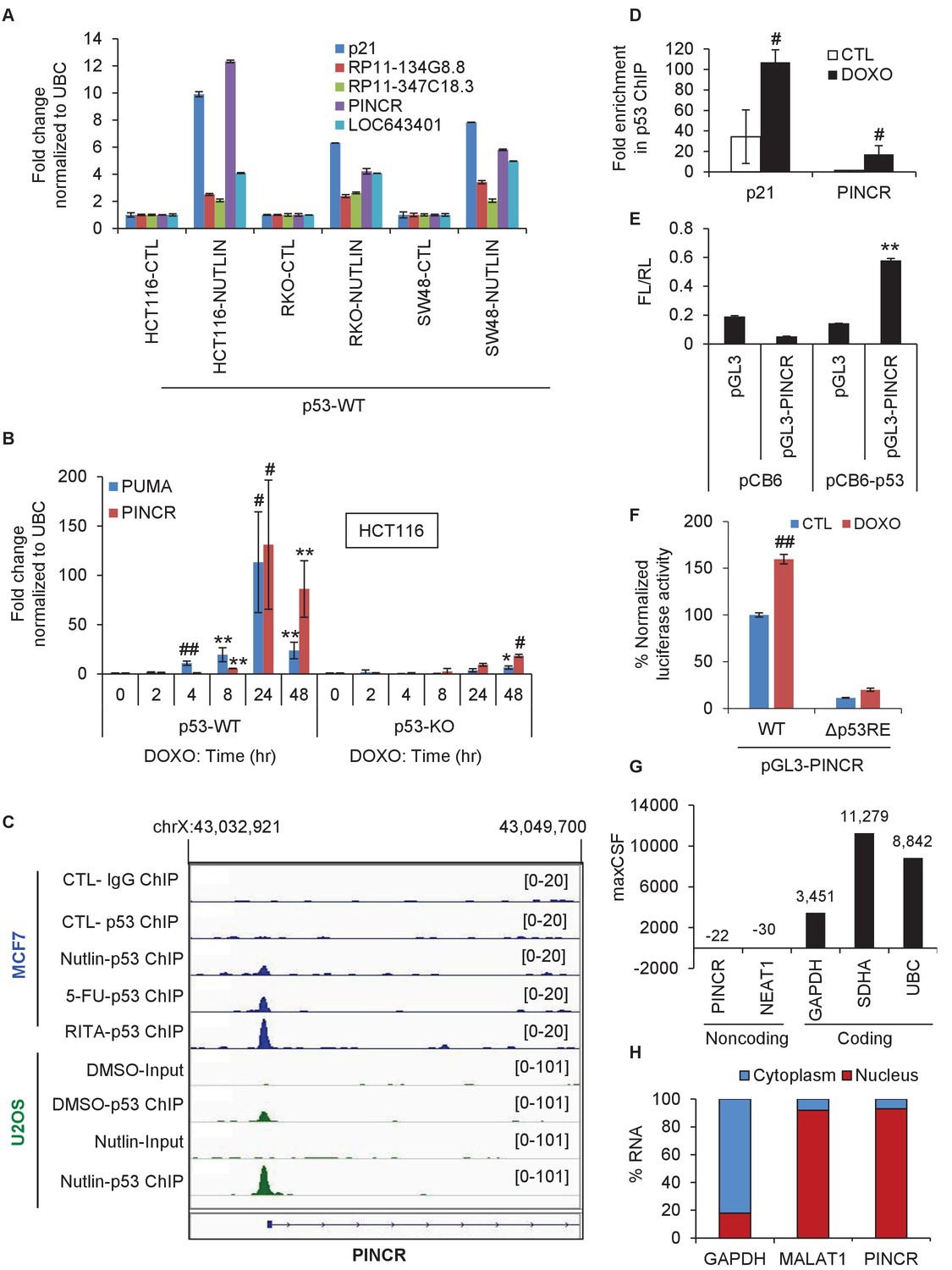
Figures and data in Prosurvival long noncoding RNA PINCR regulates a subset of p53 targets in human colorectal cancer cells by binding to Matrin 3 | eLife

PUMA-mediated copanlisib-induced apoptosis. A WT and PUMA-KO HCT116... | Download Scientific Diagram
PUMA induction by crizotinib is largely dependent on p53. A, HCT116... | Download Scientific Diagram

Regulation of p53 Stability and Function in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells* - Journal of Biological Chemistry

p300 regulates p53-dependent apoptosis after DNA damage in colorectal cancer cells by modulation of PUMA/p21 levels | PNAS
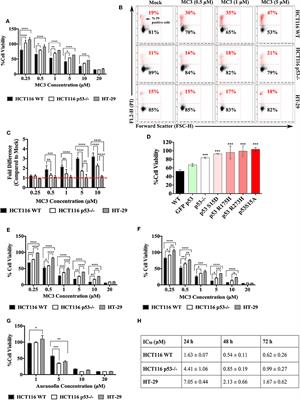
Frontiers | p53-Dependent Anti-Proliferative and Pro-Apoptotic Effects of a Gold(I) N-Heterocyclic Carbene (NHC) Complex in Colorectal Cancer Cells | Oncology

PUMA Dissociates Bax and Bcl-XL to Induce Apoptosis in Colon Cancer Cells* - Journal of Biological Chemistry
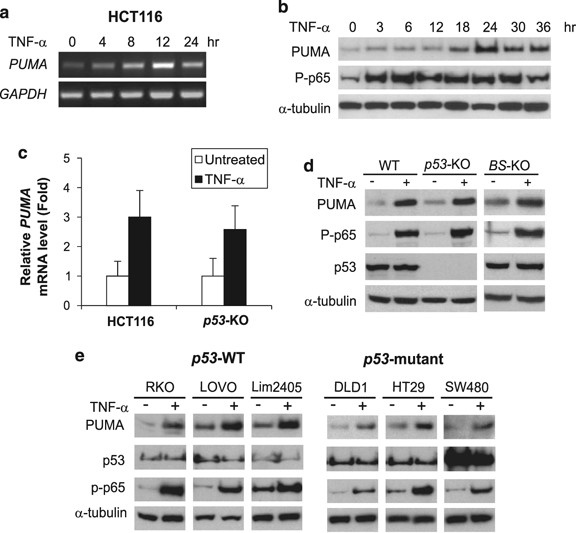
PUMA is directly activated by NF-κB and contributes to TNF-α-induced apoptosis | Cell Death & Differentiation